An easily digestible overview of ISO 13485 and how it applies to your medical device company.

If ISO 13485 solely sounds like a random assortment of letters and numbers, don't worry, you are not alone and have come to the right place!
In this blog we will do a complete breakdown of ISO 13485:2016, leaving you feeling confident and empowered to take the next steps with your medical device!
Let’s start with the basics.
What is ISO 13485?
ISO stands for International Standards Organization, and covers best practices that are globally recognized by several medical device markets around the world. ISO 13485: 2016 is the most recent version of ISO 13485, the preceding version being ISO 13485: 2003. All ISO standards are reviewed every 5 years to establish if a revision is needed in order to keep it relevant for the most current marketplace.
ISO 13485:2016 is an international standard for Quality Management Systems (QMS) of medical device manufacturers and providers. ISO 13485 specifies requirements for your QMS of your medical device and is designed to respond to latest QMS practices, including changes in technology and regulatory requirements and expectations.
If you wish to distribute your medical device across the European Economic Area (EEA), it is good to know that ISO 13485 is the QMS standard accepted as the basis for CE marking medical devices under European Directives and Regulations.
Learn how ISO 13485 can help you attain CE Marking for your Medical Device
Who can use ISO 13485?
This global standard can be utilized by medical device manufactures that are in one or more of the following medical device lifecycle stages:
- Design and Development
- Production
- Storage and Distribution
- Installation and Servicing
- Final Decommissioning and Disposal of Medical Devices
It can also be used by suppliers or other external parties providing products such as:
- Raw Materials
- Components and Subassemblies
- Medical Devices
- Sterilization Services
- Calibration Services
- Distribution Services
- Maintenance Services
Common terms used in ISO 13485
- “As appropriate” - the requirement is deemed appropriate unless the organization can determine otherwise.
- “Risk” - safety or performance requirements of the medical device or meeting applicable regulatory requirements.
- “Documented” - Records of the establishment, implementation, and maintenance of a requirement.
- “Product” - Any product or service that is intended for or required by a customer.
- “Regulatory Requirements” - Requirements by law.
- “Resource” - Anything that is needed to make the product or service, such as people, buildings, equipment, etc.
- “Shall” - Indicates a requirement.
- “Should” - Indicates a recommendation.
- “May” - Indicates a permission.
- “Can” - Indicates a possibility or capability.
ISO 13485 Clauses
There are 8 Clauses in ISO 13485, each with multiple detailed subclauses.
- Scope
- An organization demonstrates its overall ability to provide medical devices and related services that consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- Indicate if requirements from clauses 6-8 apply to your organization, and if they don’t, provide a justification of why not.
- References
- ISO 9000: 2015
- QMS
- Fundamentals
- Vocabulary
- Terms and Definitions
- ISO 9000 + a specific list of additional terms and definitions in this clause.
- Quality Management System (QMS)
- Where general requirements begin.
- Management Responsibility
- Ensures that top management actively participates in the QMS.
- Resource Management
- Ensures that top management manages resources.
- Top management must manage resources, as well as the infrastructure, so that a quality product can be produced.
- Product Realization
- How a company realizes the product, how your product comes to life, and how it will be delivered to your customer.
- Measurement, Analysis, and Improvement
- How to improve your product, your manufacturing process, and your QMS.
The chart below includes each of the 8 clauses with their appropriate subclauses:
| Clause | Subclauses |
| 1.0 Scope | No subclauses |
| 2.0 References | No subclauses |
| 3.0 Terms and Definitions | No subclauses |
| 4.0 Quality Management System |
|
| 5.0 Management Responsibility |
|
| 6.0 Resource Management |
|
| 7.0 Product Realization |
|
| 8.0 Measurement, Analysis, and Improvement |
|
How does ISO 13485 work?
13485:2016 prioritizes a risk-based approach and cites related standards, for example, ISO 14971 for managing medical device product risk management.
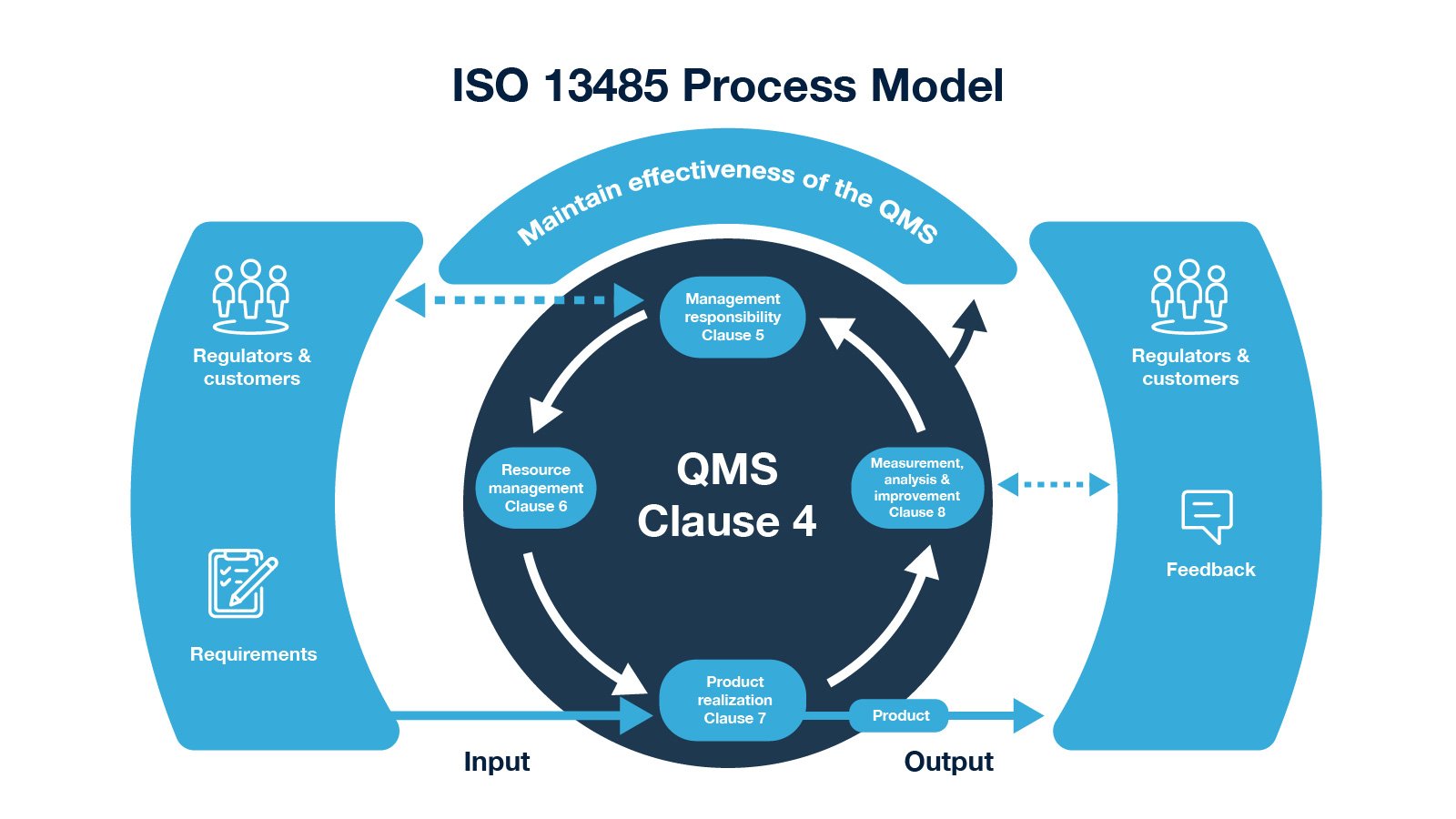
ISO 13485:2016 standard keeps both regulators and customers in one group, from the requirements for product realization and feedback, to measurement, analysis, and improvement. Moreover, the management responsibility function of the quality management system also interacts with both regulators and customers as shown in the illustration below.
Fig. 1: ISO 13485 Process Model from ISO 13485 - Regulatory Requirements on Medical Devices blog.
Why should you be conformant with ISO 13485?
ISO 13485:2016 is used by Regulatory Authorities in many other countries, thus adopting this standard will open up the opportunity for you to market your medical device in other countries besides the US as well as acquire a "globally harmonized" QMS (FDA).
Being conformant to this standard also ensures that you are compliant with FDA regulation, killing 2 birds with 1 stone. The primary focus in the latest edition of ISO 13485 is regulatory compliance and in reality, an organization cannot conform to ISO 13485 in its true sense unless the applicable regulatory requirements are met first. Thus, it is important for both medical startups and established companies to embrace this standard, which is in the market to protect public health interest. Additionally, non-compliance (whether deliberate or not) can result in grave consequences ranging from expensive fines, to a ban on marketing products, etc.
The FDA is shifting its regulations from CFR Part 820 to more closely resemble ISO 13485, because it recognizes the advantages of using globally accepted best practices for medical device QMS. Conforming to this standard will prepare you for that shift. To learn more about this shift, as well as the comparison between ISO 13485 and CFR Part 820, check out our blog ISO 13485 vs. CFR Part 820.
How do I implement ISO 13485?
One of the important steps in ISO 13485 implementation, and becoming more vigorous in approaching the market, is complying with regulatory requirements. With compliance to regulatory requirements, an organization will be prepared to offer products which are safe, and avoid the setbacks (and disadvantages) related with noncompliance.
The optimized solution to reduce risk, maintain quality, and accelerate innovation is by utilizing an FDA compliant and best practice conformant medical device quality management application. Sierra Quality Management System (QMS) offers you a robust start to identify relevant regulatory requirements, and to evaluate your company’s level of compliance.
Sierra QMS is designed for organizations who are looking to market medical devices in a global regulated environment. It is built for engineering teams to operate with their preferred tool-sets while automating the compliance with medical device QMS principles for global markets. Sierra Labs helps both medical device software developers and SaMDs developers to build a vigorous QMS that includes a variety of effective workflow management tools.
Want to see how Sierra QMS can help your organization conquer ISO 13485?
Download our free White Paper to learn more!