A quick and easy rundown of ISO and IEC standards.

Digital health-care applications help patients control chronic conditions by allowing both physicians and patients to monitor the health conditions as treatment proceeds. This is made possible with the software's capability to robustly communicate between patients, healthcare providers, and payers. Digital health-care applications offer a data-driven environment to empower life-saving decisions.
Interaction of different International Standards for Software Development
In a digital data-driven world, medical devices either include a software component or are a stand-alone software in itself on a mobile device, known as software as a medical device (SaMD). SaMDs will usually function in a contiguous ecosystem, making them inherently central in that they receive data from medical devices, of which can be connected via the communications network.
There are various ISO (International Organization for Standardization) / IEC (International Electro technical Commission) standards that help in developing and implementing medical device software.
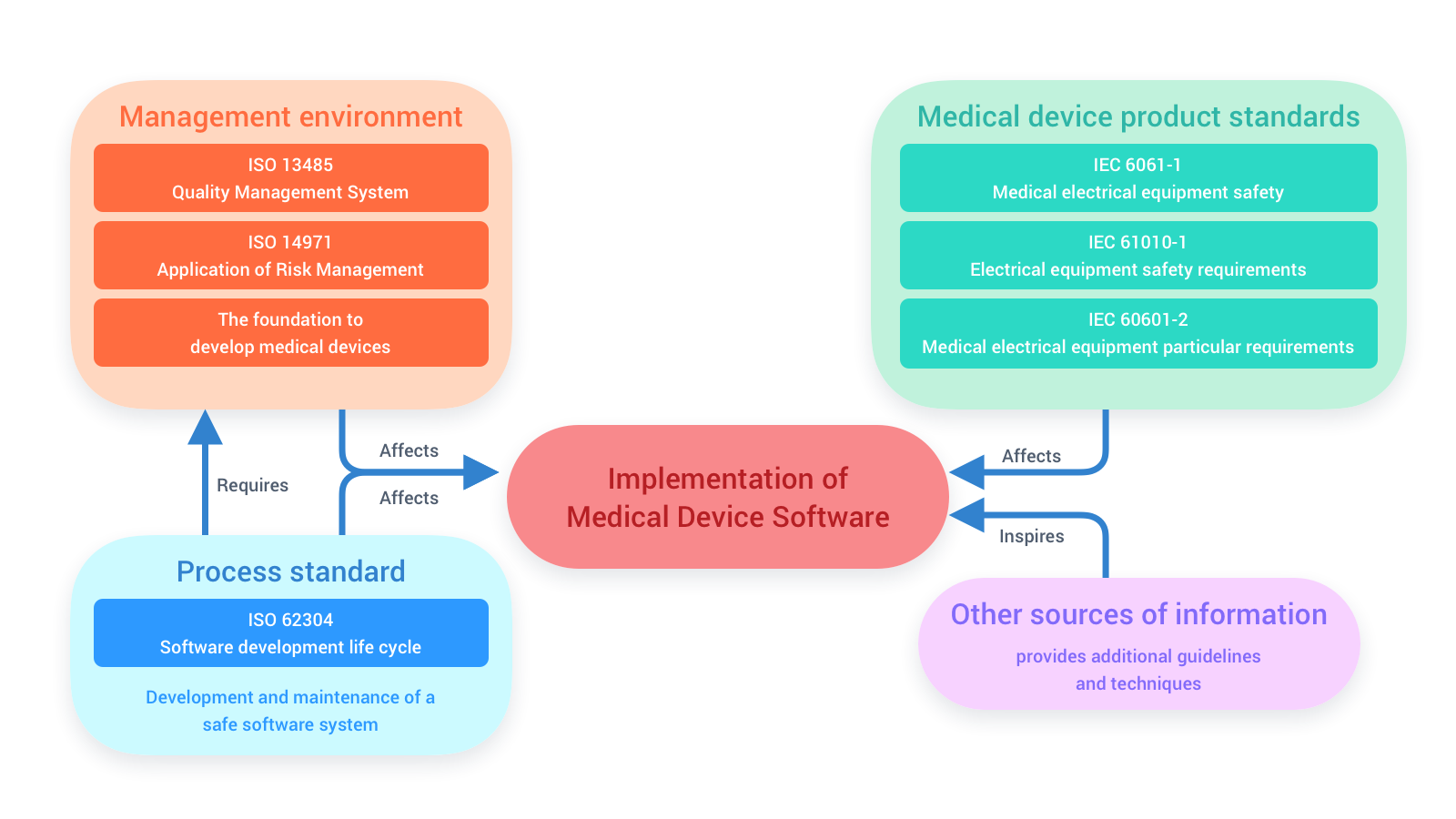
ISO 13485 and ISO 14971 provide a management system for the development of medical devices software; ISO/IEC 62304 is an international standard which explicates the process of the software development lifecycle. If the software interacts electrically with equipment, IEC 60601-1 and IEC 60601-2 are the product standards which enlighten electrical equipment safety requirements and other particular requirements related to electrical equipment. Altogether, these standards affect the development of a medical device software or development of a software as a medical device (SaMD). Therefore, the effectiveness of these standards is vital for the success of medical device software.
It is understandable that software developers may face challenges in interpreting regulatory linguistics and often times will hire regulatory professionals (or consultants) internally to help get through the approval pathway. We strongly urge that the technology leadership familiarises these concepts to allow for effective engagement with the regulatory departments and agencies.
The IEC 62304 Standard and FDA Level of Concern
IEC 62304 identifies various requirements for software development based on the classification model. The classification model of IEC 62304 matches well with FDA level of concern.
You can find all of the various requirements of IEC 62304 expressed in this checklist, as per the class of the medical device software.
| IEC 62304 Standard | FDA’s Level of Concern | Impact |
| Class A | Minor | No possibility of damage to health |
| Class B | Moderate | Possibility of non-serious injury |
| Class C | Major | Possibility of death or serious injury |
Table 1: Relationship Matrix between IEC 62304 Classifications and FDA Level of Concern
SaMDs Classification
SaMDs classification is structured on the basis of the risk possessed by the specific software as a medical device. You can find SaMDs’ categorization and classification consistent with FDA Guidance documents in its own blog, A Simple Guide to SaMD.
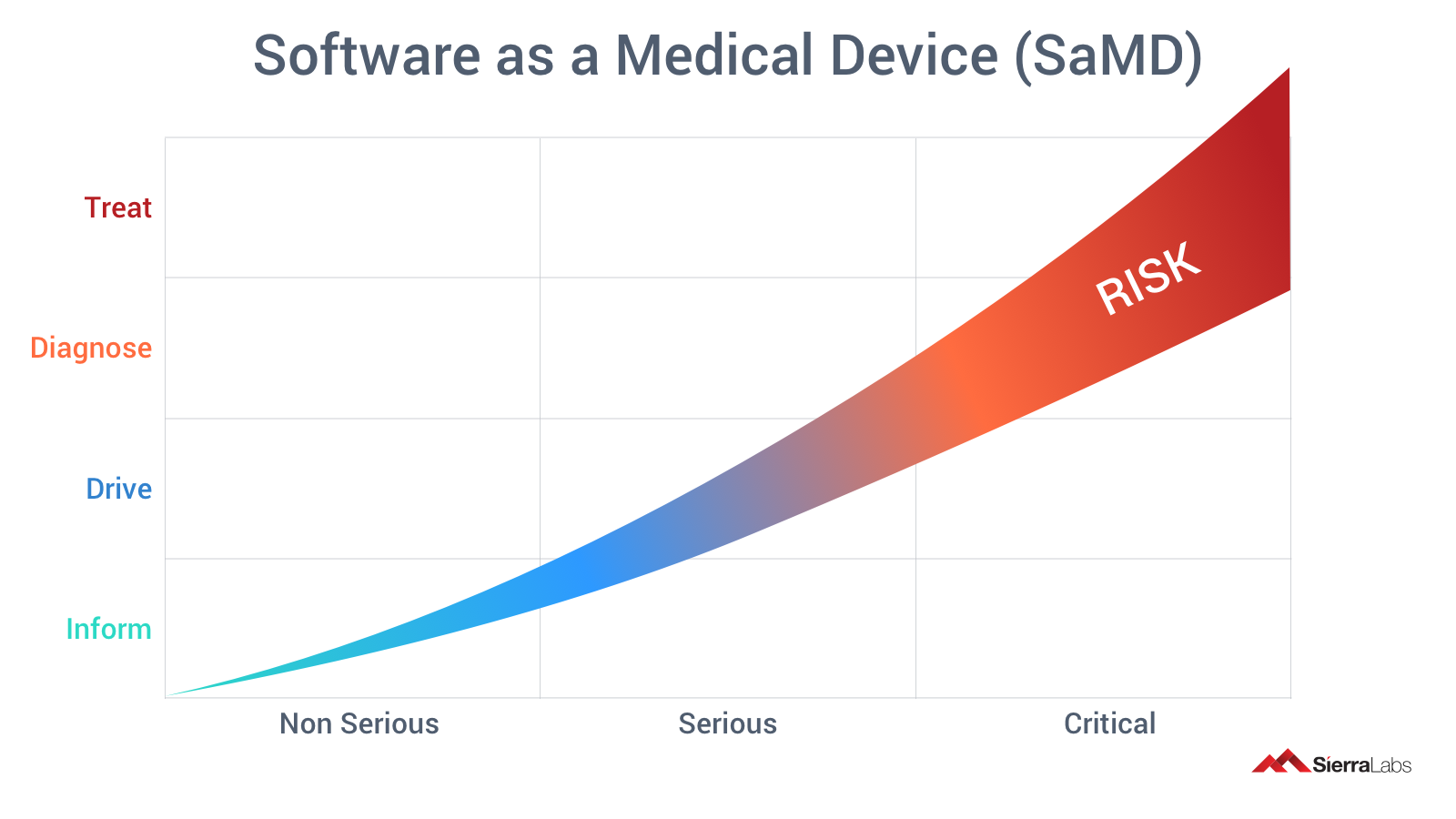
“Critical" concern will demand more documentation requirements by the FDA compared to "serious" healthcare concerns and expectedly "non-serious” concerns, which will demand lesser documentation and other requirements. Software medical device manufacturers should be in constant collaboration with the FDA and regulatory experts, due to the ever changing landscape of standards and regulations as well as an increase in changes in recent times.
Quality Management System for Medical Software Developing Companies
Now that you have learned all about the international standards for Medical Device Software and SaMDs, along with their rigorous requirements from FDA based on their classifications, let’s talk about ways to breeze through these requirements with an effective QMS!
The optimized solution to reduce risk, maintain quality, and accelerate innovation is by utilizing an FDA compliant and best practice conformant medical device quality management application. Sierra Quality Management System (QMS) allows you to have conformity AND compliance in your production process.
Sierra QMS is a QMS for life sciences that is specifically designed for organizations who are looking to market medical devices in a global regulated environment. It is built for engineering teams to operate with their preferred tool-sets while automating the compliance with medical device QMS principles for global markets. Sierra Labs helps both medical device software developers and SaMDs developers to build a robust QMS that includes a variety of effective workflow management tools.
Want to see how Sierra QMS can help your organization achieve Conformity AND Compliance?
Download our free White Paper to learn more!

